A diet rich in fish WAS one of the best sources of Omega 3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, known for their health benefits. Note that I said ‘WAS’ and not ‘IT IS’ since pollution and the contamination of our oceans with mercury, polycarbonate bisphenols (PBC) and other nuclear toxic waste become a big concern for our living environment, including marine life.
![fishoil[1]](https://mariofit1.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/fishoil1.jpg?w=244&h=137) By now, most of us are probably familiar with the health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids, (Eicosapentaenoic Acid – EPA) and Docosahexaenoic Acid – DHA) readily available from oily fish or fish oil such as: cod liver, herring, mackerel, salmon and sardine.
By now, most of us are probably familiar with the health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids, (Eicosapentaenoic Acid – EPA) and Docosahexaenoic Acid – DHA) readily available from oily fish or fish oil such as: cod liver, herring, mackerel, salmon and sardine.
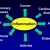
If you don’t, know much about the benefits of Omega-3, just consider the review done at the University of Maryland Medical Centre, that show the effectiveness of Omega 3 fatty acids in combating high cholesterol, high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematous (SLE), osteoporosis, depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), cognitive decline, skin disorders, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), asthma, macular degeneration, menstrual pain, colon cancer, breast cancer and prostate cancer, just to name a few. The entire article can be founded at this link: http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/omega-3-000316.htm
- DHA is so important since is the primary structural component of the human brain and retina in the eye.
- EPA become also essential to health because acts as a precursor for anti-inflammatory hormone-like substances that participate in a wide range of body functions such as the contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle, the dilation and constriction of blood vessels, control of blood pressure, and modulation of inflammation.
For general health it is recommended a minimum of 650 mg of combined EPA + DHA per day up to a safe limit of 3000 mg per day. But due to the increased level of bioaccumulation of toxins in the fish, the same health authorities recommend no more than 2 servings of fish per week, and if you are pregnant women you should avoid fish totally. And according to many environment agencies, the mercury contamination should be less than 0.5 microgram per kilogram of body weight. But this makes it difficult to get the recommended amount of omega-3s from diet alone without exposure to dangerous contaminants, which can affect our health.
![515px-MercuryFoodChain-01[1]](https://mariofit1.files.wordpress.com/2014/03/515px-mercuryfoodchain-011.png?w=246&h=287) And as I mention on my previous article: ‘Omega 3 Fish Oil and Inflammation’ (published March 17, 2014) mercury and PBC are neurotoxins which are hard to be eliminated from the body since accumulates through the food chain in a process called bioaccumulation.
And as I mention on my previous article: ‘Omega 3 Fish Oil and Inflammation’ (published March 17, 2014) mercury and PBC are neurotoxins which are hard to be eliminated from the body since accumulates through the food chain in a process called bioaccumulation.
There is also a big concern about the purity and quality of the fish oil supplements as trace levels of PCBs were found in many product tested by Consumer Lab – a leading provider of independent product testing helping consumers and healthcare professionals make safe and knowledgeable purchasing decisions. Also the August 2012 Consumer Lab report on the quality of fish oil / omega-3 supplements revealed that some supplements exceeded contaminations limits for PCBs, while others contained 20% to 30% less than the claimed amounts of EPA, DHA or other omega-3 fatty acids. One softgel product contained spoiled fish oil, while an enteric-coated softgel (intended to reduce “fish burp”) released its fish oil too early.
![USANA-BiOmega-352x198[1]](https://mariofit1.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/usana-biomega-352x1981.jpg?w=700) This is why I recommend Biomega-3 from USANA Health Sciences. It has been thoroughly tested, evaluated and given the respected stamp of approval by ConsumerLab.com. USANA’s BiOmega contains 1050 mg of EPA+DHA (1200 total omega-3 fatty acids) in a daily dose of two gel caps and without contamination. Plus, with USANA’s BiOmega, you get some extra vitamin D, but without the fishy aftertaste due to the added lemon oil.
This is why I recommend Biomega-3 from USANA Health Sciences. It has been thoroughly tested, evaluated and given the respected stamp of approval by ConsumerLab.com. USANA’s BiOmega contains 1050 mg of EPA+DHA (1200 total omega-3 fatty acids) in a daily dose of two gel caps and without contamination. Plus, with USANA’s BiOmega, you get some extra vitamin D, but without the fishy aftertaste due to the added lemon oil.
This picture speaks for itself: ![1221250192[1]](https://mariofit1.files.wordpress.com/2014/04/12212501921.jpg?w=700)